CNC machining, or milling, is one of the most common industry techniques used in precision component manufacturing. The CNC machine shaves away material according to a CAD design, resulting in high accuracy for finished components and products.
What’s the difference between a 3, 4, and 5-axis CNC milling machine? Which process suits your machining project, providing the best results? The core difference between 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis CNC machining is the range of motion used in the milling process.
A 3-axis milling machine keeps the cutting tool on a fixed path, while the tool can change position in 4 and 5-axis machines. For instance, a 4-axis machine adds 360°rotations in the horizontal cutting plane. All three machines operate on an X, Y, & Z axis. However, a 4-axis CNC milling machine includes the addition of an A cutting axis. The 5-axis CNC milling machine includes the addition of a B & C cutting axis.
The addition of axes to the CNC milling process, improves the potential for complex component and product design and manufacturing. However, the more axes the machine has, the higher its price tag.
3-Axis CNC Milling Machines
While 3-axis CNC machining is the simplest of the three options, it’s the most widely available and commonly used. The simplicity of the machine and its capabilities shouldn’t be overlooked, as it’s more than capable of creating precision comments in a range of industries.
In a 3-axis CNC milling machine, the operator fixes the workpiece in a single position during the cutting process. The spindle operates along an X, Y, and Z axis in a linear direction. It’s common for machine shops to use a 3-axis milling machine to produce simple components.
It’s a great machine for producing components that aren’t deep, but it struggles to cut a narrow cavity. These jobs are labor-intensive and don’t produce perfect finishes on final components. The 3-axis CNC milling machine is better suited to drillings, planar milled profiles, and threaded holes in-line with an X, Y, or Z axis.
4-Axis CNC Milling Machines
The 4-axis CNC milling machine brings the addition of an “A” axis. The spindle features three linear axes of motion (X, Y, Z), as in 3-axis CNC machines. The addition of the A-axis occurs through workpiece rotation.
There are several arrangements for the 4-axis CNC milling machine. However, they are vertical movements with the spindle rotation moving around the Z-axis. After mounting to the X-axis, it rotates around the A-axis.
4-axis CNC milling is an economically viable method of machining components theoretically achievable on a standard 3-axis CNC machine. Manufacturers get faster machining times and improved accuracy over using a 3-axis machine.
5 axis cnc machining
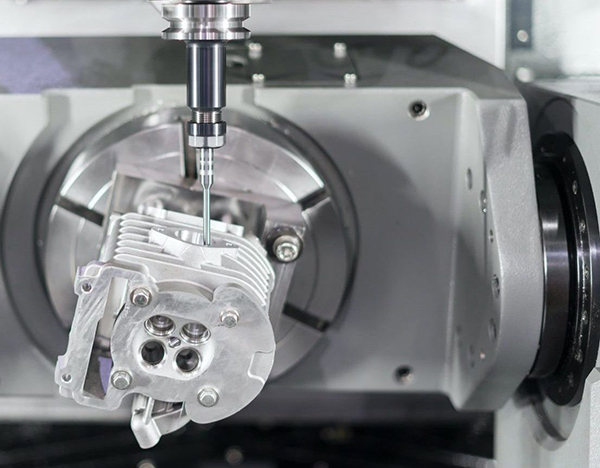
5-Axis CNC Milling Machines
The 5-axis CNC milling machine utilizes two of three possible rotations depending on the machine model. The machine relies on rotation in the B & C or A & C axes. The workpieces rotation around these five axes occurs through spindle or workpiece manipulation, according to the CAD design.
5-axis CNC milling machines can process alternate sides of the workpiece without changing its position on the table. As a result of the additional cutting axes, operators experience higher levels of efficiency when cutting prismatic components.
The versatile nature of 5-axis CNC milling machines makes them ideal for creating precision products and parts in the following industries.
- Aerospace components.
- Medical components.
- Military components and products.
- Gas and oil mechanical components.
Manufacturers must bear in mind that while there are several benefits to implementing 5-axis CNC machining over 3 and 4-axis machines, not all components are suitable for cutting on 5-axis machines.
Likewise, components better suited to 3-axis machining might not be suitable for 5-axis machining. Your choice of CNC method should fit your project requirements and costs.
